Development documentation
Implementation
Implementation of supported use cases in the core component:
- Initialize core component.
- Execute operation.
- Register result listener.
- Get administration interface.
How to implement a plugin provider:
Internal configuration
Logging
pineapple-core uses log4j for logging. Each pineapple client must provide a Log4j configuration which is accessible at runtime as a result of the build process.
The core component does not provide a Log4j configuration as part of its production build. A log4j configuration file is defined in the project in the directory src/test/resources/log4.properties for testing.
The test configuration configures Log4j to write to the log file to ${user.home}/.pineapple/logs/pineapple.log.
Spring configuration file(s)
The core component contains a configuration file which defines a Spring application context. The Spring application context defines dependency injection of objects as part of initialization of the core component. The file is located in src/main/resources/com.alpha.pineapple.core-config.xml.
Test beans for integration tests
The spring application context defines a test profile named integration-test whose beans are only added to the context when a test class activates the profile through the usage of the profile Id integration-test, e.g. @ActiveProfiles("integration-test"):
<beans profile="integration-test" >
<bean id="ObjectMotherCredentialProvider" class="com.alpha.testutils.ObjectMotherCredentialProvider" />
</beans>
Implementation
Core classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple contains public interface and classes of the core component:
- PineappleCore defines the public interface of the core component. It exposes operations for registration of result listeners and for execution of operations.
- CoreImpl is the implementation of the PineappleCore interface. The main class in the core component.
- CoreException is an exception class for signaling errors in the core component.
- CoreFactory implements public factory class for creation of pineapple core component instances.
CoreFactory
The factory class can be created in two ways:
- Use the new operator.
- From the core Spring application context.
If the factory is created using the new operator its dependencies isn't injected:
- uninitializedPineappleCore
- uninitializedFileBasedCredentialProvider
- runtimeDirectoryResolver
The factory will at runtime validate whether the dependencies are resolved, if not the factory will load the core Spring application context and resolve them by if self.
The factory is idempotent in regard to creation to of core and provider instances since they are defined with default scope in the Spring context.
Core administration classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.admin contains public interface and classes for runtime administration of the core component:
- AdministrationProviderImpl implements the public interface of the core component administration API, e.g. the Administration interface. It exposes operations for accessing the internal repository classes of the core component for runtime configuration. The class also implements the AdministrationProvider interface which is used to expose the administration API to plugins.
Credential handling classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.credential contains classes used to provide credentials to Pineapple resources. The credentials are used to access and authenticate the application with external resources:
- ConfigurationInfo interface to represent information about an credential configuration in the credential provider.
- ConfigurationInfoImpl is the default implementation of the ConfigurationInfo interface which is used by the FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl class.
- EnvironmentInfoImpl is the default implementation of the EnvironmentInfo interface which is used by the FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl class.
- CredentialInfoImpl is the default implementation of the CredentialInfo interface which is used by the FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl class.
- CredentialInfoFactory defines interface for creation of credential info objects which implements the CredentialInfo interface.
- CredentialConfigurationMarshaller defines interface for loading and saving credentials from file. Furthermore the marshaller defines methods for mapping loaded models objects from the package com.alpha.pineapple.model.configuration into info objects, e.g. ConfigurationInfo, EnvironmentInfo and CredentialInfo.
- CredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl implements the CredentialConfigurationMarshaller interface.
- FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl implements the CredentialProvider interface which initializes credentials from a XML file. The provider uses JAXB to load and save data from XML to objects from the package com.alpha.pineapple.model.configuration. The actual loading and saving is delegated to the configured credential configuration marshaller.
- CredentialsFileNotFoundException is an exception class for signaling failures during loading of credentials in credential provider.
The package com.alpha.pineapple.credential.encryption contains classes used to encrypt passwords stored in the crendetials.xml file and keep the passwords encrypted when read into memory:
- PasswordEncryptingCredentialInfoFactoryImpl implements the CredentialInfoFactory interface. the factory implements creation of credential info objects with encrypted passwords.
- PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl implements the CredentialConfigurationMarshaller interface. The marshaller supports loading and saving of credentials to file while encrypting all passwords.
- FileBasedPasswordPBEConfigImpl implements the PBEConfig interface which defines a configuration object for a Jasypt StandardPBEStringEncryptor encryptor. The configuration object supports loading of a password file defined by the JVM system property pineapple.credentialprovider.password.file to set the encryptor master password.
Encrypting credential passwords
Credential passwords should be encrypted. The goal of the design is to achieve:
- All credential passwords stored in memory should be encrypted.
- Passwords should only exist decrypted in memory when used by the core component to establish a session to a resource.
- All credential passwords stored on disk in the credentials.xml file should be encrypted.
The design realizes these use cases to support the encryption requirements:
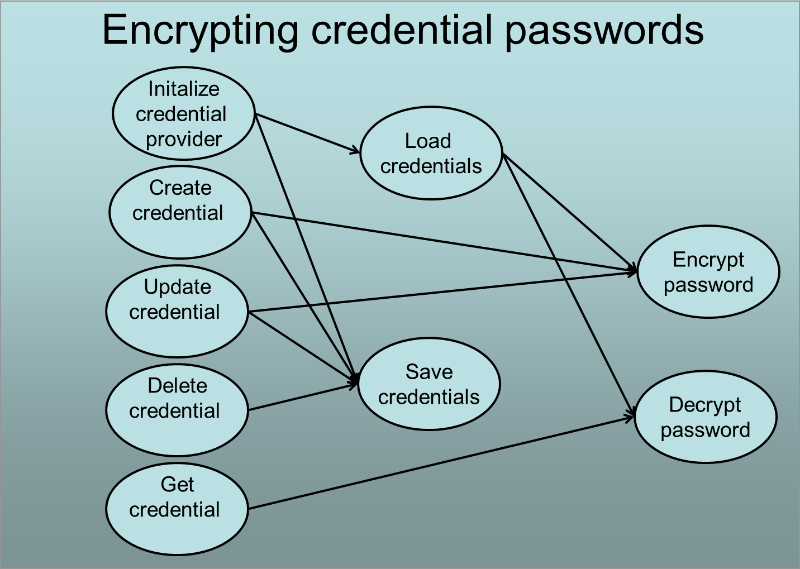
When Initialize credential provider is performed: The credentials are loaded from the credentials.xml:
- A password without the prefix encrypted: is encrypted and stored in memory encrypted with the prefix.
- A password with the prefix encrypted: is read into memory. The password is decrypted to validate that value after the prefix is in fact a encrypted value. If the decryption succeeds then decrypted password is thrown away. If the decryption fails then the value after the prefix is interpreted as a unencrypted password, the password is encrypted and stored encrypted in memory with the prefix.
- If an unencrypted password was encountered then the credentials is written back to file:
- To synchronize the in-memory representation and the file content.
- To encrypt the unencrypted password immediately.
When Create credential is performed: The credential is created with the password is encrypted with the prefix encrypted: and stored in-memory encrypted. The configuration is saved to synchronize the in-memory representation and the file content. Encryption is handled from FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl which delegates the creation of CredentialInfo to a CredentialInfoFactory where the password is encrypted prior to storing it in the credential info.
When Update credential is performed: The credential is deleted and then a new credential is created. The password is encrypted with the prefix encrypted: and stored in-memory encrypted. The configuration is saved to synchronize the in-memory representation and the file content. Encryption is handled from FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl which delegates the creation of CredentialInfo to a CredentialInfoFactory where the password is encrypted prior to storing it in the credential info.
When Delete credential is performed: The credential is deleted. The configuration is saved to synchronize the in-memory representation and the file content.
When Get credential is performed: Decryption is done by delegating the Credential creation to the CredentialConfigurationMarshaller in this case the PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl. The method is only invoked when the core component creates a session to a resource.
The FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl delegates the Load credentials and Save credentials to its configured mashaller which is PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl. The marshaller handles the encryption cases described above and then delegates the loading, saving and mapping to the CredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl. The result is that all encryption functionality can be isolated to two classes; PasswordEncryptingCredentialInfoFactoryImpl and PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl.
PasswordEncryptingCredentialInfoFactoryImpl
Factory for creation of credential info objects with encrypted passwords. The factory supports creation of objects which implements the CredentialInfo interface. The factory creates objects of the type CredentialInfoImpl. When a credential info object is created the password is encrypted and prefixed with encrypted: prefix.
The factory is used by the PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl class and the FileBasedCredentialProviderImpl class to support encryption of passwords in memory and on disk.
PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl
The marshaller is the central class in the design to support encryption of credential passwords.
The marshaller delegates the main bulk of load, saving and mapping logic to the CredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl class and only intercepts calls when encryption is required.
Encrypting the Jasypt master password
The symmetric encryption functionality used by PasswordEncryptingCredentialInfoFactoryImpl and PasswordEncryptingCredentialConfigurationMarshallerImpl to encrypt credential passwords is implemented through the usage of the Jasypt string encryptor StandardPBEStringEncryptor.
The encryptor is configured to receive its configuration from the configuration object FileBasedPasswordPBEConfigImpl. The configuration object implements the Jasypt PBEConfig interface which defines a configuration object for a StandardPBEStringEncryptor encryptor.
The configuration object implements this algorithm to resolve the password:
- The directory for the credential provider password file is resolved from the runtime directory provider:
- If the system property pineapple.credentialprovider.password.file is set then its value is interpreted as the location of the file.
- If the system property isn't defined then the file is resolved to ${pineapple.home.dir}/conf/credentialprovider.password.
- If the password file doesn't exists then the file is created with a random generated password which is created using UUID.randomUUID(). The password is written to the file using UTF-8 encoding.
- The password is read from the file using UTF-8 encoding and returned.
Configuration of Jasypt in Spring
Encryption of credential passwords are implemented through usage of the Jasypt library.
The symmetric password encryptor StandardPBEStringEncryptor is used. The encryptor is configured in the spring configuration file with a fixed salt. The salt is required to be fixed to support usage of the encryptor across JVM restarts.
The password for the encryptor is resolved by the CredentialProviderPasswordEnvironmentPBEConfigImpl class which loads the password from an external password file (read the class description below for more details).
Module classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.module contains classes for representation and storage of modules:
- ModuleInfoImpl is the default implementation of the ModuleInfo interface which is used by the DirectoryBasedModuleRepositoryImpl class.
- DirectoryBasedModuleRepository extends the ModuleRepository interface for directory based module implementations.
- DirectoryBasedModuleRepositoryImpl implements the <<<DirectoryBasedModuleRepository interface for directory based module repository implementations.
- ModuleRepositoryInitalizationFailedException defines exception to signal error during module repository initialization.
DirectoryBasedModuleRepositoryImpl
The repository administers a set of available modules resolved from the modules directory. The modules directory is resolved from the runtime directory provider.
The class is defined as a bean in the application context for the core component. The instance created by the the context is not initialized. The repository is initialized by invoking the initialize() method. This method can be invoked from clients to refresh to content of the repository.
Resource classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.resource contains classes for storage of information about resources defined in the environment configuration:
- ConfigurationInfo interface to represent information about an environment configuration in the resource repository.
- ConfigurationInfoImpl is the default implementation of the ConfigurationInfo interface which is used by the ResourceRepositoryImpl class.
- EnvironmentInfoImpl is the default implementation of the EnvironmentInfo interface which is used by the ResourceRepositoryImpl class.
- ResourceInfoImpl is the default implementation of the ResourceInfo interface which is used by the ResourceRepositoryImpl class.
- ResourceConfigurationMarshaller interface for loading an environment configuration (as XML) from disk into info objects. And versus visa.
- ResourceConfigurationMarshallerImpl is the default implementation of the ResourceConfigurationMarshallerImpl interface which is used by the ResourceRepositoryImpl class.
- ResourcePropertyInfoImpl is the default implementation of the ResourcePropertyInfo interface which is used by the ResourceRepositoryImpl class.
- ResourceRepositoryImpl is the default implementation of the ResourceRepository interface.
ResourceRepositoryImpl
The repository administers the set of configured resources in the environment configuration.
The repository support resolution of resources using a wild card environment. The name of the wild card environment is *. The used algorithm of resolution of a resource is, e.g. get(E,R):
- if repository contains environment E and the resource R is defined in the environment then E.R is returned.
- if repository contains environment * and the resource R is defined in the environment then *.R is returned.
- if repository doesn't contain environment E then an exception is thrown.
- if repository doesn't contain resource E.R then an exception is thrown.
ResourceConfigurationMarshallerImpl
The marshaller supports mapping from the unmarshalled configuration classes to the internal representation using the info objects. It also support mapping from the info classes to the configuration class used for marshalling.
Finally it supports the save operation which enables the repository to save the resource configuration on updates to the repository.
Plugin repository classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.repository contains classes for storage of information about registered plugins:
- PluginInfo defines interface for info about a configured plugin. Plugin info's are stored in the plugin repository.
- PluginInfoImpl is the default implementation of the PluginInfo interface which is used by the PluginRepositoryImpl class.
- PluginRuntimeRepository extends the PluginRepository interface from the API project. The interface defines runtime methods for the repository which contains information about all registered plugins resources in the environment configuration.
- PluginRepositoryImpl is the default implementation of the PluginRuntimeRepository interface.
- PluginNameGeneratorImpl is a Spring Bean id generator which generates names for plugin candidates during plugin candidate scanning.
- SessionNameGeneratorImpl is a Spring Bean id generator which generates names for session classes during plugin candidate scanning.
- OperationNameGeneratorImpl is a Spring Bean id generator which generates names for operation classes during plugin candidate scanning.
- PluginCandidateScanner defines interface for scanner which implements scanning of plugin candidates in a list of packages.
- PluginCandidateScannerImpl is the default implementation of the PluginCandidateScanner interface.
- PluginInitializer defines interface for initializer which can initialize a plugin candidate into a ready-to-use plugin.
- PluginInitializerImpl is the default implementation of the PluginInitializer interface.
Separation of the plugin repository interface into two parts
The overall interface for the plugin repository is split into interfaces, PluginRepository and PluginRuntimeRepository, to be able to include a public interface (e.g. PluginRepository) in the Administration API (exposed through the API project) and define a internal interface for the core core component (e.g. PluginRuntimeRepository) which contains implementation specific details for resolution and execution of plugins at runtime.
Inclusion of the implementation specific details (e.g. stuff like OXM marshallers) in the public interface would resulted in the inclusion of Spring Framework interfaces (e.g. again the OXM marshallers) in the API project. This would have bloated the dependency graph for the API project and this was deemed unwise and thus the interface was split into two.
PluginRepositoryImpl
The class is defined as a bean in the application context for the core component. The instance created by the the context is not initialized. The repository is initialized by invoking the method: PluginRepository.initialize( String[] pluginIds );. The method is invoked in the InitializePluginActivatorCommand.
The repository will only scan for plugins candidates in the packages which is defined in the collection of plugin id's supplied as arguments to the initialize(..). The actual scanning is delegated to the PluginCandidateScannerImpl.
After a list of plugin candidates have been identified and stored in a application context. Then each candidate is processed in turn by the PluginInitializerImpl which attempts to initialize the candidate as a plugin.
The repository support resolution of operations using a wild card operation. The name of the wild card operation is *. The used algorithm of resolution of an operation is, e.g. get(P,O):
- if repository contains plugin P is defined and operation for O is defined then P.O is returned.
- if repository contains plugin P is defined and operation for * is defined then P.* is returned.
- if repository doesn't contain plugin P then an exception is thrown.
- if repository doesn't contain operation P.O then an exception is thrown.
PluginNameGeneratorImpl
Implements the BeanNameGenerator interface. The class is used by the PluginCandidateScannerImpl during scanning of the class path for plugin candidates in the scanForPlugins(..) method to generate bean names for plugin candidates.
The class generates names of the form: plugin: package-name.
PluginCandidateScannerImpl
The class is used by the PluginRepositoryImpl to scan the class path for plugin candidates.
The scanner will only scan for plugins candidates in the packages which is defined in the collection of plugin id's supplied as arguments to the scanForPlugins(..). The scanning criteria's is defined as:
- Scan for classes with the @Plugin annotation.
- Scan the packages is supplied as arguments to the initialize(..) method.
The scanner returns the collection of identified plugin candidates stored as beans in a application context. The bean id's are generated by the PluginNameGeneratorImpl class.
PluginInitializerImpl
The class is used by the PluginRepositoryImpl to initialize plugin candidates into ready-to-use plugins.
The initializer initializes plugins from the metadata defined on the @Plugin..
The initializer initializes the plugin application context with plugin providers which provides access to the Pineapple runtime system. These providers are initialized:
- The execution info provider with bean id = "coreExecutionInfoProvider".
- The runtime directory provider with bean id = "coreRuntimeDirectoryProvider".
- The administration provider with bean id = "coreAdminitrationProvider".
Execution classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.execution contains classes for storage of information about execution of operation on modules:
- ExecutioninfoImpl is the default implementation of the ExecutionInfo interface.
- ResultRepositoryImpl is default implementation of the ResultRepository interface which creates execution result objects which collect information about execution of operations on modules. The repository also has the role of subject in the observer pattern where interested parties can register themselves for notification when operations are executed.
- OperationTaskImpl is default implementation of the OperationTask interface which supports the initialization and synchronous execution of an operation by delegation of requests to a collection of command objects.
- AsyncOperationTaskImpl is implementation of the OperationTask interface which supports synchronous execution of an operation.
- ExecutionInfoProviderImpl is default implementation of the ExecutionInfoProvider and ExecutionInfoProviderAdministration interfaces. The class is injected into plugins. The object is used by plugins to gain access to the execution info object for the current operation.
- ExecutionInfoNotFoundException is exception class used to signal errors in attempts to lookup ExecutionInfo in ExecutionInfoProviderImpl .
- ExecutionContextRepository defines interface for context repository which defines a central storage of operation context during the execution of a operation. Context are stored for access by plugin providers (such as the execution info provider and the variable substitution provider).
- ExecutionContextRepositoryImpl is default implementation if the ExecutionContextRepository interface. The class is used by the OperationTaksImpl which stores and removes contexts.
- ResourceResolver defines interface for resolution of target resources.
- DefaultResourceResolverImpl is the default implementation of the ResourceResolver interface. Supports resolution of resources from lists and regular expressions.
- OperationResolver defines interface for resolution of target operation.
- DefaultOperationResolverImpl is the default implementation of the OperationResolver interface. supports resolution of whether a operation should be restricted from execution of a current model. The resolution of is based on the value of the target-operation attribute on models.
ExecutionContextRepositoryImpl
Repository for storage of execution contexts. The execution context for an operation is stored and removed from the repository during execution by OperationTaskImpl.
The algorithm for looking up a execution context in get(ExecutionResult) is:
- Lookup context using the result object as argument.
- If the lookup failed, then inspect whether result object is root. If the result object is root return null.
- Get parent result object and invoke get(..) with the parent result as argument.
The repository is accessed during execution by the plugin providers:
- Execution info provider
- Variable substitution provider
ResultRepositoryImpl
When an operation is started by the core component then the repository is used to create a ExecutionInfo meta data object which described the executed operation. In addition to the meta data, the execution info object also contains a reference to the root ExecutionResult object which contains the state of the execution.
The result repository implements the role of subscriber in the publish-subscriber pattern. Subscribers are all the registered result listeners, which implements the ResultListener interface.
When a execution result changes it state all registered listeners are notified of the event. The notification is done by invoking the ResultListener.notify(ExecutionResultNotification notification) on each listener with the state changing result as argument.
Besides notifying all registered listeners, repository also captures the events for the executing operations. The event capture is used by the REST controller in the web application to be able to deliver updated results when polled by a client (e.g. a controlling Pineapple instance).
The repository is implemented with a fixed capacity to limit the amount for stored executions in the repository. The repository has capacity for a fixed number of completed executions and any number of running executions. The fixed number of completed executions is defined by the the hard coded constant CoreConstants.EXECUTION_HISTORY_CAPACITY which initially is set to 5.
AsyncOperationTaskImpl
The implementation of the asynchronous execution is implemented by the usage of the Spring annotation @Async:
@Async
@Override
public void execute(ExecutionInfo info) {
operationTask.execute(info);
}
@Override
public ExecutionInfo execute(String operation, String environment, String module) {
String message = messageProvider.getMessage("aot.unspported_method");
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(message);
}
@Override
public ExecutionInfo executeComposite(String operation, String environment, String module, String description, ExecutionResult result) {
String message = messageProvider.getMessage("aot.unspported_method");
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(message);
}
The configuration of the underlying task executor is defined in the Spring application context com.alpha.pineapple.core-config.xml by the operationExecutor bean.
The class forwards requests to the OperationTaskImpl which implements synchronous execution of a operation.
Only the method execute(ExecutionInfo info) support asynchronous execution of an operation. The other two methods defined in the interface throws an UnsupportedOperationException.
ExecutionInfoProviderImpl
The object implements the interface ExecutionInfoProvider is used by plugins to look up runtime info.
The algorithm for looking up up runtime info in the ExecutionInfoProvider.get(ExecutionResult result) method is:
- Lookup up the execution context for the operation in the execution context repository. The result is used as argument. The execution context for an operation is registered in the context by the OperationTaskImpl.
- Lookup the execution info in the context. The result is used as argument. The execution info for an operation was registered in the context by the InitializeOperationCommand.
- If the lookup fails then a ExecutionInfoNotFoundException is thrown.
The class is made available to plugins through usage of the @Resource dependency injection with either the bean or field id "coreExecutionInfoProvider". The class is made available to the core component through definition in the core component application context.
Scheduled execution classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.execution.scheduled contains the classes which defines the scheduled execution of operations:
- ScheduledOperationConfigurationMarshaller defines interface for loading and saving configuration scheduled operations.
- ScheduledOperationConfigurationMarshallerImpl is the default implementation of the ScheduledOperationConfigurationMarshaller which support saving and loading the set of scheduled operations (as XML).
- ScheduledOperationInfoImpl is the default implementation of the ScheduledOperationInfo interface which defines metadata for a scheduled operation within the Pineapple core. The actual scheduling of the operation is implemented by the ScheduledOperationRespositoryImpl
- ScheduledOperationRespositoryImpl is the default implementation of the ScheduledOperationRespository interface which manages and contains information about all scheduled operations.
- ScheduledOperationNotFoundException is a runtime exception thrown by the repository when queried for an non existing operation.
- ScheduledOperationAlreadyExistsException is a runtime exception thrown by the repository when an operation already is registered with the same ID.
Trigger execution classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.execution.trigger contains the classes which defines the synchronous execution of triggers:
- OperationTriggerResolver defines interface for resolution of trigger(s) to execute for a model. The trigger candidate list is resolved versus the expected target operation.
- ResultTriggerResolver defines interface for resolution of trigger(s) to execute for a model. The trigger candidate list is resolved versus the expected execution state.
- DefaultOperationTriggerResolverImpl implements the OperationTriggerResolver interface.
- DefaultResultTriggerResolverImpl implements the ResultTriggerResolver interface.
DefaultOperationTriggerResolverImpl
Resolves whether a trigger should be executed. The resolution is based on the algorithm:
- If the value of the on-target-operation attribute is null.
- If the value of the on-target-operation attribute is empty.
- If the value of the on-target-operation attribute is the wild card value "*".
- If the value of the on-target-operation attribute is identical to the operation that the model was invoked with.
- If the value of the on-target-operation attribute is a list value and one of the values in the list is identical to the operation that the model was invoked with.
DefaultResultTriggerResolverImpl
Resolves whether a trigger should be executed. The resolution is based on the algorithm:
- If the value of the on-result attribute is null.
- If the value of the on-result attribute is empty.
- If the value of the on-result attribute is the wild card value "*".
- If the value of the on-result attribute is identical to the result that the model execution concluded with.
- If the value of the on-result attribute is a list value and one of the values in the list is identical to the result that the model execution concluded with.
Directory resolution
The package com.alpha.pineapple.io.file contains helper classes for resolution of directories:
- DefaultRuntimeDirectoryProviderImpl implements the RuntimeDirectoryProvider interface which is used to resolve the default runtime directories where Pineapple will run from. The runtime directory provider is injected into the application context for each initialized plugin to provide runtime info about the configured of the used directories.
DefaultRuntimeDirectoryProviderImpl
Default implementation of the RuntimeDirectoryProvider interface which is used to resolve the default resolve runtime directories where Pineapple will run from.
The class is made available to plugins through usage of the @Resource dependency injection with either the bean or field id coreRuntimeDirectoryProvider.
Resolution of the home directory
The home directory is resolved using the algorithm:
- If the system property pineapple.home.dir is set then the home directory is resolved to this directory.
- If the system property isn't defined then Pineapple will resolve to its home directory to: ${user.home}/.pineapple
The operating system is determined on the value of the os.name system property.
${user.home} is the value of the user.home system property.
Resolution of the temp directory
The temp directory is resolved from the system property java.io.tempdir.
Resolution of the credential provider master password file
The location of the password file is resolved using the algorithm:
- If the system property pineapple.credentialprovider.password.file is set then its value is interpreted as the location of the file.
- If the system property isn't defined then the file is resolved to ${pineapple.home.dir}/conf/credentialprovider.password.
Resolution of model paths
To support location independent model element path (MEP) within module models the provider can resolve these path prefixes:
- modulepath: resolves the path to the root of the current module. This can be used to define the location of files within a module in a location independent way .
- moduleroot: resolves the path to the root of another module. This can be used to define the location of files within another module in a location independent way .
Plugin activation classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.activation contains classes for invocation of plugins at runtime:
- PluginActivator defines interface for plugin activator which is used at runtime to provide access to external resources through sessions and operations.
- PluginActivatorImpl implements the PluginActivator interface.
PluginActivatorImpl
The class is defined as a bean in the application context for the core component. The instance created by the the context is not initialized. The activator is initialized by invoking the method: PluginActivator.initialize( CredentialProvider provider, ResourceRepository resourceRepository, PluginRepository pluginRepository );.
The method is invoked in the InitializePluginActivatorCommand.
Session handling classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.session contains classes for handling session management during invocation of plugin operations:
- SessionHandlerFactory defines a interface for session handler factories.
- RetrySessionHandlerFactoryImpl defines a factory class for creation of RetrySessionHandlerImpl instances.
- RetrySessionHandlerImpl implements the Operation interface which is used to decorate plugin operations which support session handling and retry logic.
RetrySessionHandlerImpl
Session handling
The purpose of the session handler is to connect the plugin session prior to invoking the operation and to disconnect afterwards. The session handler achieves its goal by proxying all plugin operations which supports input marshalling. Proxying a plugin operation with a session handler is done by the PluginActivator.
Retry logic
To support retry logic on a session operations, all sessions are proxied using the SessionRetryProxyFactoryImpl.
Tunneling exceptions
When an exception occurs in the session handler then the exception is caught and rethrown immediately in a RuntimeException. The purpose of the runtime exception is to channel the exception to the invoking InvokePluginsCommand. The InvokePluginsCommand will catch the exception and process the embedded exception appropriately by setting an error message and completing the operation result with the Error state.
The RetrySessionHandlerImpl supports tunneling of these exceptions:
- SessionConnectException thrown when an error occurs during connecting to a plugin session.
- SessionDisconnectException thrown when an error occurs during disconnecting from a plugin session.
- SessionException thrown when an error occurs during usage of a connected session.
- PluginExecutionFailedException thrown when an error occurs during execution of a plugin.
- IllegalArgument thrown when validation of a method argument fails within some plugin code.
Implementation note: The InvokePluginsCommand exception clause must mirror these exception to be able to handle them.
Enabling usage of the session handler as a Spring bean
Plugin operation classes are proxied at runtime by the RetrySessionHandlerImpl class. The session handler class implements session handling for an operation and retry logic.
To enable usage of the RetrySessionHandlerImpl as a Spring managed bean for a which a new instance (e.g. a Spring prototype bean) is created every time an operation is proxied, several beans are defined. The beans defined to support the usage of RetrySessionHandlerImpl are:
<bean id="unintializedRetrySessionHandler" class="com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.session.SessionRetryHandlerImpl" scope="prototype"/>
<bean id="springRetrySessionHandlerFactory" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ObjectFactoryCreatingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetBeanName">
<idref local="unintializedRetrySessionHandler"/>
</property>
</bean>
The springRetrySessionHandlerFactory bean is a factory for creation of Spring managed objects. The factory supports creation of instances of the referenced bean unintializedSessionHandler.
The unintializedRetrySessionHandler bean is defined to define a target object for the factory. The bean is defined as a prototype. It should NOT be used directly as a dependency.
Session retry classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.session.retry contains classes session retry support implemented using the Spring Retry project:
- SessionRetryListener extends the Spring Retry RetryListener interface to support registration of a execution result to capture any retry information.
- SessionRetryListenerImpl implements the SessionRetryListener interface.
- SessionRetryProxyFactory defines interface for for factory which supports creation of object proxies which implements session retry logic.
- SessionRetryProxyFactoryImpl implements the SessionRetryProxyFactory interface. The factory supports programmatic creation af a session proxy which implements retry logic using the Spring Retry.
SessionRetryListenerImpl
The listener class logs method retries and add the information to the registered execution result. The listener is able to differentiate between cause of the retry, e.g. whether it is caused by a connect, usage or disconnect error.
The class is defined as a bean named sessionRetryListener in the application context for the core component. The bean is registered with the RetryTemplate which implements the retry logic. The bean is registered as part of constructing a session proxy done by the SessionRetryProxyFactoryImpl class.
SessionRetryProxyFactoryImpl
Factory for creation of session retry proxy instances. The factory supports creation of JDK dynamic proxies using the Spring ProxyFactory. The proxy factory doesn't support creation of proxies for session classes with NO no-arg constructor (e.g. the defined constructors which requires arguments).
The factory creates the session proxy programmatically by:
- Creates a SessionRetryListenerImp instance and registers the execution result for the operation.
- Creates a RetryTemplate and registers the session retry listener.
- Creates a RretryOperationsInterceptor and registers the retry template.
- instruments the target session with the retryOperationsInterceptor bean.
Spring configuration of retry support
The core component application context defines retry support with these beans:
<bean id="sessionRetryProxyFactory" class="com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.session.retry.SessionRetryProxyFactoryImpl" />
<bean id="sessionRetryListener" class=" com.alpha.pineapple.plugin.session.retry.SessionRetryListenerImpl" scope="prototype" />
<bean id="simpleRetryPolicy" class="org.springframework.retry.policy.SimpleRetryPolicy">
<property name="maxAttempts" value="4"/>
</bean>
<bean id="exponentialBackOffPolicy" class="org.springframework.retry.backoff.ExponentialBackOffPolicy" >
<property name="initialInterval" value="100"/>
<property name="maxInterval" value="5000"/>
<property name="multiplier" value="2"/>
</bean>
<bean id="retryTemplate" class="org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate" scope="prototype">
<property name="retryPolicy" ref="simpleRetryPolicy" />
<property name="backOffPolicy" ref="exponentialBackOffPolicy" />
</bean>
<bean id="retryOperationsInterceptor" class="org.springframework.retry.interceptor.RetryOperationsInterceptor" scope="prototype">
</bean>
<bean id="springRetryTemplateFactory" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ObjectFactoryCreatingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetBeanName">
<idref local="retryTemplate"/>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="sessionRetryListenerFactory" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ObjectFactoryCreatingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetBeanName">
<idref local="sessionRetryListener"/>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="springRetryOperationsInterceptorFactory" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ObjectFactoryCreatingFactoryBean">
<property name="targetBeanName">
<idref local="retryOperationsInterceptor"/>
</property>
</bean>
The defined beans are:
- The sessionRetryProxyFactory bean enables usage of the sessionRetryProxyFactoryImpl class as a Spring managed bean.
- The sessionRetryListener bean enables usage of the SessionRetryListenerImpl class as a Spring managed bean.
- The simpleRetryPolicy bean configures the retry policy for the setup. A SimpleRetryPolicy is used which will trigger reinvocation of a failed method with a preset number of attempts. The policy is configured with 4 attempts. This will allow the retry support to capture three succesive exception and then a hopefully successful attempt.
- The exponentialBackOffPolicy bean defines a back off policy which calculates the pauses between attempts.
- The retryTemplate bean implements the Spring retry engine. It uses the retry policy and back off policy to directs its behavior.
- The retryOperationsInterceptor bean defines a AOP advice which is used on proxied classes. The advice intercepts all method invocations, including toString().
- The springRetryTemplateFactory bean enables programmatic creation of the Spring managed bean retryTemplate.
- The sessionRetryListenerFactory bean enables programmatic creation of the Spring managed bean sessionRetryListener.
- The springRetryOperationsInterceptorFactory bean enables programmatic creation of the Spring managed bean retryOperationsInterceptor.
Commands classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.command contains classes which implements the org.apache.commons.chain.Command interface. The commands are implementations of the GOF design pattern and the serve many purposes:
- CommandFacade defines interface for usage of commands within the core component.
- CommandFacadeImpl is default implementation of the CommandFacade interface. Use commands through this class.
- CreateDefaultEnvironmentConfigurationCommand creates default environment configuration files (resurces.xml and credentails.xml) if none exist and unpacks examples modules into the created modules directory.
- CopyExampleModulesCommand unpacks which copies example modules into the modules directory in a generated default configuration.
- InitializeOperationCommand initializes execution of an operation.
- InitializePluginActivatorCommand initializes the plugin activator class. The plugin activator is initialized with resource implementation info and a credential provider.
- InvokePluginsCommand implements execution of a operation on a module.
- InvokeTriggersCommand implements execution of a triggers defined in a module model.
- MarshallJAXBObjectsCommand can marshall objects to a XML file using JAXB. The root object of the object graph from the context is written to file. The command that the file name defines an absolute path.
- UnmarshallJAXBObjectsCommand can unmarshall objects from an XML file using JAXB. The root object of the unmarshalled objects is stored in the context.
CommandFacadeImpl
The facade object provides a facade for the command objects. Thus the facade has references to the commands objects. But the individual command objects also uses the facade to invoke other commands. Thus the command objects has references to the facade.
This introduces circular dependencies between the facade and the command objects.
To enable Spring to handle the circular dependencies, the command objects are on the facade set using using setter injection. The same applies to the usage of setter injection on the commands to set the facade.
InvokePluginsCommand
Tunneling exceptions
The command supports capture of tunneled exception thrown in a session handler.
The InvokePluginsCommand will catch the exception and process the embedded exception appropriately by setting an error message and completing the operation result with the Error state.
The InvokePluginsCommand supports capture of these tunneled exceptions:
- SessionConnectException thrown when an error occurs during connecting to a plugin session.
- SessionDisconnectException thrown when an error occurs during disconnecting from a plugin session.
- SessionException thrown when an error occurs during usage of a connected session. s * PluginExecutionFailedException thrown when an error occurs during execution of a plugin.
- IllegalArgument thrown when validation of a method argument fails within some plugin code.
Variable substitution classes
The package com.alpha.pineapple.substitution contains classes for variable substitution in files and models:
- VariableSubstitutionProviderImpl implements the VariableSubstitutionProvider interface and provides functionality for variable substitution of artifacts (e.g. text and files) in plugins. When the provider substitutes the content of an artifact then a substitution result is added to the supplied parent result. If substitution process fails then an exception is thrown but the failures will also be reflected in the validation execution result (and its children).
- VariableResolver defines interface for runtime resolution of variables.
- DefaultVariableResolverImpl implements the VariableResolver interface which support variable substitution using the Commons StrSubstitutor.
- ModelVariableSubstitutor defines interface for runtime resolution of variables in loaded models. Variable substitution is supported through proxying the model and intercepting all calls which returns strings.
- ModelVariableSubstitutorImpl implements the ModelVariableSubstitutor interface.
The package com.alpha.pineapple.substitution.proxy contains classes for proxying a unmarshalled model object graph to support variable substitution of models:
- VariableSubstitutedProxyFactory defines interface for factory which supports creation of object proxies which supports variable substitution.
- VariableSubstitutedProxyFactoryImpl implements the VariableSubstitutedProxyFactory interface.
- VariableSubstitutionInterceptor implements the MethodInterceptor interface. This class is a Spring AOP advice which the created proxies are configured to invoke whenever at method is invoked.
The package com.alpha.pineapple.substitution.variables contains classes for collecting variables from different sources which constitutes the input to the variable substitution process:
- Variables defines interface for set of variables intended for usage in variable substitution.
- DefaultVariablesImpl implements the Variables interface.
- VariablesBuilder defines interface for variables builder which can build a variables object used for variable substitution.
- NullVariablesBuilderImpl implements the VariablesBuilder interface which returns an empty variables object.
- ResourceVariablesBuilder extends the VariablesBuilder interface to support initialization of a model Resource as input.
- ResourceVariablesBuilderImpl implements the ResourceVariablesBuilder interface which returns a variables object which contains the variables defined in a Resource instance.
- ModelVariablesBuilder extends the VariablesBuilder interface to support initialization of model as input.
- ModelVariablesBuilderImpl implements the ModelVariablesBuilder interface which returns a variables object which contains the variables defined in a Model instance.
- ModuleDescriptorVariablesBuilder extends the VariablesBuilder interface to support initialization of module descriptor as input.
- ModuleDescriptorVariablesBuilderImpl implements the ModuleDescriptorVariablesBuilder interface which returns a variables object which contains the variables defined in a Module instance.
- CompositeVariablesBuilder extends the VariablesBuilder interface to support initialization of variable builders to setup the composite.
- CompositeVariablesBuilderImpl implements the CompositeVariablesBuilder interface builds build variables from any number of variable builders.
Variable builders are registered by name in the order of their precedence, i.e. the variables defined by the first registered builder takes precedence of the variables defined in the secondly registered builder. When building the variables instance, then variables from the first registered builder are added first, then variables from the second registered builder are added afterwards.
If a builder defines a variable which is already defined through the processing of an earlier builder (maybe with the same value or not) then it ignored, e.g. a variable takes presence from the order of which the builders are registered.
Builders are added by name. When the variables instance is built then all variables in a builder will also be registered with the builder name as a prefix. Example: If a builder is registered with the name "model" and it defines two variables v1=a and v2=b. Then the building will result in the registration of four variables: model.v1=a, v1=a, model.v2=b and v2=b. Prefixed variables are processed for all builder builders prior to processing non-prefixed variables. This is ensure prefixed variables takes precedence over non preficed variables.
ModelVariableSubstitutorImpl
Implements the ModelVariableSubstitutor interface and provides the variable substitution capabilities in models.
The main idea behind the variable substitution is to proxy the object graph which represents the marshalled XML model and to intercept all calls to the object graph:
- Calls which returns a String are processed for variables.
- Calls which return a non-immutable object, instead returns a proxy.
- Calls which return an immutable object are ignored, i.e the immutable eobject is returned.
- Calls which return an primitive are ignored, i.e the primitive is returned.
The responsibility of the ModelVariableSubstitutorImpl is to:
- Assemble the variable builders support lookup of variables defined in module descriptors, the model and in the resource properties:
- Variables defined in the module descriptor are handled by an instance of the ModuleDescriptorVariablesBuilder
- Variables defined in the model are handled by an instance of the ModelVariablesBuilder
- Variables defined in the session resource properties are handled by an instance of the SessionVariablesBuilder
- Initialize the proxying of the model by initializing the proxy factory VariableSubstitutedProxyFactory.
VariableSubstitutionInterceptor
This class is a Spring AOP advice. It it used by the proxy factory VariableSubstitutedProxyFactoryImpl to intercept all method calls to objects which are proxied by JDK dynamic proxies.
When it intercepts a method it implements the algorithm:
- If the return type of the invoked method is a String then:
- Invoke the object and get the returned string.
- Process the string for variables.
- Return the string.
- Otherwise:
- Invoke the object and get the returned object.
- Decorate the returned result with a new proxy, using the proxy factory to create to proxy, the and return the proxy.
CglibVariableSubstitutionInterceptorImpl
This class is a Spring CGLIB AOP advice. It it used by the proxy factory VariableSubstitutedProxyFactoryImpl to intercept all method calls to objects which are proxied by JDK dynamic proxies.
It implements the same algorithm as VariableSubstitutionInterceptor for variable processing.
VariableSubstitutedProxyFactoryImpl
Factory for creation of proxy instances depending on the implementation of the target class which should be proxied.
The factory implements the algorithm:
- If the target object is null then return null.
- If the target object is a string then process the string for variables and return the processed string.
- If the target object is immutable then return the target object unchanged.
- If the target object is a primitive then return the target object unchanged.
- If the target object is a private class then create a JDK dynamic proxy using the Spring ProxyFactory.
- Otherwise create a dynamic proxy using CGLIB. The actual creation of the proxy is done using Objenesis library to handle the case where the class doesn't have a no-arg constructor (e.g. the defined constructors which requires arguments). Objenesis is used since it supports object creation while the bypassing constructor(s).
Unit test of the project
Commonly used constants in the unit tests are defined in the class com.alpha.testutils.CoreTestConstants.
Helper classes
Helper classes:
- com.alpha.testutils.ObjectMotherResourceRepository
- com.alpha.testutils.ObjectMotherCredentialProvider
Integration test Spring configuration class
The package com.alpha.spring.config contains Spring helper classes.
The class IntegrationTestSpringConfig defines a Java based spring configuration which is used by integration tests.
The configuration is used by including it in the test class:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ActiveProfiles("integration-test")
@ContextHierarchy({ @ContextConfiguration(locations = { "/com.alpha.pineapple.core-config.xml" }),
@ContextConfiguration(classes = IntegrationTestSpringConfig.class) })
public class PluginActivatorImplIntegrationTest {
/**
* Object mother for credential provider
*/
@Resource
ObjectMotherCredentialProvider providerMother;
....
}
Test files
The file src/test/resources/resources.xml contains and environment configuration file which defines a resource using the TestResource:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<environments>
<environment>
<identifier>localdomain</identifier>
<resources>
<test-resource>
<identifier>test-resource-resourceidentifier</identifier>
<credential-identifier>test-resource-credentialidentifier</credential-identifier>
<plugin>com.alpha.pineapple.resource.test.TestFactoryImpl</plugin>
</test-resource>
</resources>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
