Pineapple Continuous Integration
This page describes the design of the continuous integration setup used to build and test the Pineapple project.
Two setups are used to develop Pineapple:
- A CI setup is implemented at Shippable.
- A local setup is implemented which can be installed as a module.
CI setup at Shippable
Shippable provides a dashboard for the CI setup at: Pineapple dashboard at Shippable\
A new build is initiated when a commit is made to the master branch.
The build creates the Pineapple Docker image and uploads it to DockerHub.
The build uploads the Pineapple binaries to Bintray.
Local CI setup
The local continuous integration setup for Pineapple consists of the components:
- JUnit will be used as test framework. At some point, it must be determined whether JUnit is suitable for implementation of larger scale system tests which involves multiple servers, Pineapple instances, agents and plugins.
- Jenkins is used as continuous integration server.
- Artifactory is used as a repository manager for management of binary artifacts.
- VirtualBox is used to provide virtualized servers to conduct tests on. VirtualBox is chosen due to its integration with Vagrant.
- Vagrant is used to provision virtual server instances.
- Docker is used to provision Docker containers within virtual server instances.
- Pineapple is used to build the setup.
Setup
The setup consists of a host machine where VirtualBox, Vagrant and Pineapple are installed. VirtualBox is used as hypervisor. Vargrant is used to define and managed virtual machines. Pineapple is used to do the initial build of the build the setup.
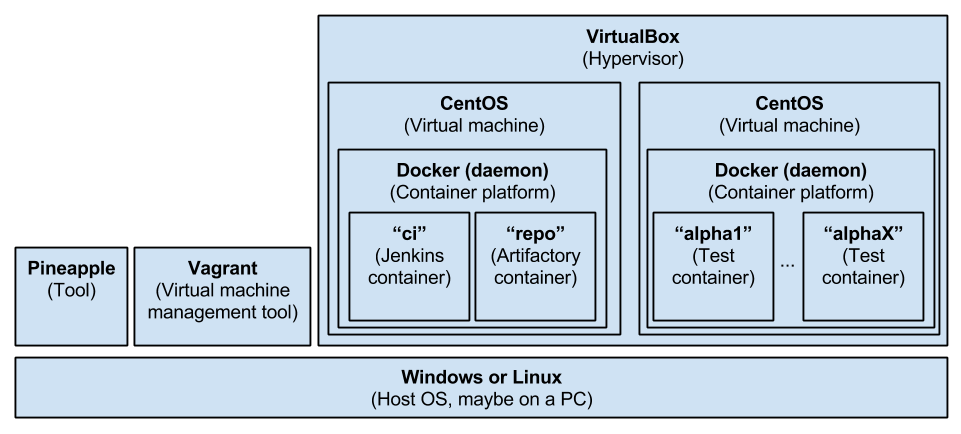
Virtual machines
Two virtual machines are hosted on VirtualBox:
- The build server VM
- The test containers VM
The build server VM
The purpose of the VM is to run a Docker host which contains Docker containers with the CI tools, e.g. Jenkins and Artifactory. The tools are setup through the creation of these Docker images:
- The CI container (named "ci") based on the official Jenkins Docker image. These software components and tools are installed on the "ci" container:
- Java Virtual Machine (JDK).
- Continuous integration server (Jenkins).
- Maven.
- The repository container (named "repo") based on the official Artifactory Docker image.
Pineapple module and environment configuration
Module
The setup is defined in the example module named xx-pineapple-dev-docker-install-ci-linux64. The module creates the setup through these steps:
- Installs Docker on both VMs
- Installs Artifactory on the build server VM
- Installs Jenkins on the build server VM
- Initializes Artifactory by uploading the system configuration and 3rd party artifacts.
Environment configuration
The environment used to install the setup is named linux-pineapple-ci.
The environment contains the definition of the resources:
- ssh-ci-node1 which defines SSH access to the build server VM at 192.168.99.10:22
- ssh-ci-node2 which defines SSH access to the test containers VM at 192.168.99.11:22
- docker-ci-node1 which defines access to the Docker host at the build server VM at 192.168.99.10:8082
- docker-ci-node2 which defines access to the Docker host at the build server VM at 192.168.99.11:8082
The environment, resources and credentials are created as part of the default configuration.
Build server VM configuration
Services
The SSH daemon is started and listens on 0.0.0.0:22.
The Docker daemon is running on 0.0.0.0:8082.
Test containers VM configuration
Services
The SSH daemon is started and listens on 0.0.0.0:22.
The Docker daemon is running on 0.0.0.0:8082.
Build server software components
Docker
Docker is installed as an OS service.
Docker listens on http://192.168.99.10:8082
Docker installation
The installation consists of these steps:
- Create Docker user. A custom docker user is created and added to the sudoers file.
- Update YUM. Update YUM packages.
- Add Docker YUM repository. Configure the Docker YUM repository with YUM.
- Install Docker. Docker is installed as a systemctrl service. The Docker daemon is configured using the configuration file etc/docker/daemon.json which defines the API to listen on /var/run/docker.sock/ and [::]:8082. The Docker systemd configuration is overridden by the systemd drop-in configuration file /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/systemd-override.conf which clears any host flags from the systemd configuration to avoid conflict with the etc/docker/daemon.json.
- The installation is validated.
Docker is configured to:
- Listen for local connections by the root user.
- Listen on 0.0.0.0:8082 to support remote usage of the REST API.
The Docker daemon configuration file daemon.json is installed in /etc/docker/daemon.json. The file configures the daemon to:
- Listen for local connections by the root user.
- Listen on 0.0.0.0:8082 to support remote usage of the REST API.
The file contains:
{
"hosts": [ "unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
"tcp://0.0.0.0:8082" ]
}
The Docker systemd is overridden by the drop-in file systemd-override.conf. The file is installed in /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/systemd-override.conf. The purpose of the file is to clear any default host flags from the systemd configuration file installed by Docker. This will avoid conflict with the etc/docker/daemon.json.
The file contains:
[Service] # This line resets / "removes" the original ExecStart as was defined in the main systemd unit file ExecStart= # This line defines the new ExecStart to use _instead_ ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd
Build server Docker images
CI container ("ci")
Docker image
The image for the CI container is based on the official Jenkins Docker image jenkins/jenkins:2.163-jdk11.
The Jenkins image is extended to support configuration of Jenkins with the Pineapple configurations and build jobs. The extension is implemented through definition of a new docker image named pineapple/ci:1.0. The dockerfile for the CI container is located in xx-pineapple-dev-docker-install-ci-linux64/dockersrc/ci
The dockerfile copies the Jenkins configuration files to the Jenkins staging directory /usr/share/jenkins/ref/. When jenkins.sh is run (as part of starting a container) then the files are copied to the /var/jenkins_home volume used by the jenkins container.
Jenkins plugins
The set of used plugins are defined in the Dockerfile for the pineapple/ci:1.0 image:
# Install plugins
RUN /usr/local/bin/install-plugins.sh \
blueocean:1.10.2 \
disk-usage:0.28 \
pipeline-maven:3.67
Jenkins admin user
The Jenkins admin user is defined in the Dockerfile for the pineapple/ci:1.0 image:
# Setting up environment variables for Jenkins admin user ENV JENKINS_USER admin ENV JENKINS_PASS admin
Docker container
The CI container is named "ci".
The CI container defines a network link to the "repo" container: repo:repository while defining the DNS name repository internally in the CI container. The DNS name is used in the settings.xml to access the different repositories.
JVM
The used Jenkins image is based on OpenJDK 11. The OpenJDK 11.x is installed in support compilation of Pineapple with Java 11.
Jenkins JVM configuration
The main Jenkins configuration file is /var/jenkins_home/config.xml is used to define the path to the JDK used for compiling build jobs:
...
<jdks>
<jdk>
<name>openjdk-11_linux-x64</name>
<home></home>
<properties>
<hudson.tools.InstallSourceProperty>
<installers>
<hudson.tools.ZipExtractionInstaller>
<url>https://download.java.net/java/ga/jdk11/openjdk-11_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz</url>
<subdir>jdk-11</subdir>
</hudson.tools.ZipExtractionInstaller>
</installers>
</hudson.tools.InstallSourceProperty>
</properties>
</jdk>
</jdks>
...
Jenkins Maven configuration
The Jenkins Maven configuration file /var/jenkins_home/hudson.tasks.Maven.xml is used to define the version of Maven to be installed and used by Jenkins for build jobs:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<hudson.tasks.Maven_-DescriptorImpl>
<installations>
<hudson.tasks.Maven_-MavenInstallation>
<name>maven-3.5.4</name>
<properties>
<hudson.tools.InstallSourceProperty>
<installers>
<hudson.tasks.Maven_-MavenInstaller>
<id>3.5.4</id>
</hudson.tasks.Maven_-MavenInstaller>
</installers>
</hudson.tools.InstallSourceProperty>
</properties>
</hudson.tasks.Maven_-MavenInstallation>
</installations>
</hudson.tasks.Maven_-DescriptorImpl>
Maven configuration
The standard Maven configuration file /var/jenkins_home/settings.xml is used to define the repositories used by Maven to resolve dependencies. The configuration file can be generated by exporting it from Artifactory.
The Maven configuration file is referenced by the pipeline in the Jenkinsfile:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.1.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.1.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.1.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<servers>
<server>
<username>admin</username>
<id>central</id>
</server>
<server>
<username>admin</username>
<id>snapshots</id>
</server>
</servers>
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<name>repo</name>
<url>http://repository:8081/artifactory/repo</url>
<id>repo</id>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<profiles>
<profile>
<repositories>
<repository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>central</id>
<name>libs-release</name>
<url>http://repository:8081/artifactory/libs-release</url>
</repository>
<repository>
<snapshots />
<id>snapshots</id>
<name>libs-snapshot</name>
<url>http://repository:8081/artifactory/libs-snapshot</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>central</id>
<name>plugins-release</name>
<url>http://repository:8081/artifactory/plugins-release</url>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<snapshots />
<id>snapshots</id>
<name>plugins-snapshot</name>
<url>http://repository:8081/artifactory/plugins-snapshot</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
<id>artifactory</id>
</profile>
</profiles>
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>artifactory</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
</settings>
Please notice that the repository is referenced throught the usage of the DNS name repository This name is made available to the CI container through network linking when the CI container is created.
Repository container ("repo")
Docker image
The image for the repository container is based on the official Artifactory OSS Docker image. The extension is implemented through definition of a new docker image named pineapple/repo:1.0. The dockerfile for the CI container is located in xx-pineapple-dev-docker-install-ci-linux64/dockersrc/repo
The image defines the data volume:
- /var/opt/jfrog/artifactory
Artifactory configuration
When the container is started, then the web service /artifactory/api/system/configuration is invoked with HTTP GET to trigger initialization of Artifactory.
After the initialization is completed, the web service /artifactory/api/system/configuration is invoked with HTTP POST to install the Artifactory system configuration from the file artifactory.config.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<config xmlns="http://artifactory.jfrog.org/xsd/1.5.3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.jfrog.org/xsd/artifactory-v1_5_3.xsd">
<offlineMode>false</offlineMode>
...
<localRepository>
<key>ext-release-local</key>
<description>Local repository for third party libraries</description>
<includesPattern>**/*</includesPattern>
<repoLayoutRef>maven-2-default</repoLayoutRef>
<enableNuGetSupport>false</enableNuGetSupport>
<enableGemsSupport>false</enableGemsSupport>
<blackedOut>false</blackedOut>
<handleReleases>true</handleReleases>
<handleSnapshots>false</handleSnapshots>
<maxUniqueSnapshots>0</maxUniqueSnapshots>
<suppressPomConsistencyChecks>false</suppressPomConsistencyChecks>
<propertySets/>
<archiveBrowsingEnabled>false</archiveBrowsingEnabled>
<snapshotVersionBehavior>unique</snapshotVersionBehavior>
<localRepoChecksumPolicyType>client-checksums</localRepoChecksumPolicyType>
<calculateYumMetadata>false</calculateYumMetadata>
<yumRootDepth>0</yumRootDepth>
</localRepository>
...
<remoteRepositories>
<remoteRepository>
<key>zk-ce</key>
<description>ZK CE repository</description>
<includesPattern>**/*</includesPattern>
<repoLayoutRef>maven-2-default</repoLayoutRef>
<enableNuGetSupport>false</enableNuGetSupport>
<enableGemsSupport>false</enableGemsSupport>
<blackedOut>false</blackedOut>
<handleReleases>true</handleReleases>
<handleSnapshots>true</handleSnapshots>
<maxUniqueSnapshots>0</maxUniqueSnapshots>
<suppressPomConsistencyChecks>false</suppressPomConsistencyChecks>
<propertySets/>
<archiveBrowsingEnabled>false</archiveBrowsingEnabled>
<url>http://mavensync.zkoss.org/maven2</url>
<offline>false</offline>
<hardFail>false</hardFail>
<storeArtifactsLocally>true</storeArtifactsLocally>
<fetchJarsEagerly>false</fetchJarsEagerly>
<fetchSourcesEagerly>false</fetchSourcesEagerly>
<retrievalCachePeriodSecs>43200</retrievalCachePeriodSecs>
<assumedOfflinePeriodSecs>300</assumedOfflinePeriodSecs>
<missedRetrievalCachePeriodSecs>7200</missedRetrievalCachePeriodSecs>
<remoteRepoChecksumPolicyType>generate-if-absent</remoteRepoChecksumPolicyType>
<unusedArtifactsCleanupPeriodHours>0</unusedArtifactsCleanupPeriodHours>
<shareConfiguration>false</shareConfiguration>
<synchronizeProperties>false</synchronizeProperties>
<listRemoteFolderItems>true</listRemoteFolderItems>
<rejectInvalidJars>false</rejectInvalidJars>
<p2Support>false</p2Support>
<p2OriginalUrl>http://mavensync.zkoss.org</p2OriginalUrl>
<socketTimeoutMillis>15000</socketTimeoutMillis>
</remoteRepository>
<remoteRepository>
<key>zk-ee</key>
<description>ZK Enterprise repository</description>
<includesPattern>**/*</includesPattern>
<repoLayoutRef>maven-2-default</repoLayoutRef>
<enableNuGetSupport>false</enableNuGetSupport>
<enableGemsSupport>false</enableGemsSupport>
<blackedOut>false</blackedOut>
<handleReleases>true</handleReleases>
<handleSnapshots>true</handleSnapshots>
<maxUniqueSnapshots>0</maxUniqueSnapshots>
<suppressPomConsistencyChecks>false</suppressPomConsistencyChecks>
<propertySets/>
<archiveBrowsingEnabled>false</archiveBrowsingEnabled>
<url>http://mavensync.zkoss.org/zk/ee-eval</url>
<offline>false</offline>
<hardFail>false</hardFail>
<storeArtifactsLocally>true</storeArtifactsLocally>
<fetchJarsEagerly>false</fetchJarsEagerly>
<fetchSourcesEagerly>false</fetchSourcesEagerly>
<retrievalCachePeriodSecs>43200</retrievalCachePeriodSecs>
<assumedOfflinePeriodSecs>300</assumedOfflinePeriodSecs>
<missedRetrievalCachePeriodSecs>7200</missedRetrievalCachePeriodSecs>
<remoteRepoChecksumPolicyType>generate-if-absent</remoteRepoChecksumPolicyType>
<unusedArtifactsCleanupPeriodHours>0</unusedArtifactsCleanupPeriodHours>
<shareConfiguration>false</shareConfiguration>
<synchronizeProperties>false</synchronizeProperties>
<listRemoteFolderItems>true</listRemoteFolderItems>
<rejectInvalidJars>false</rejectInvalidJars>
<p2Support>false</p2Support>
<p2OriginalUrl>http://mavensync.zkoss.org</p2OriginalUrl>
<socketTimeoutMillis>15000</socketTimeoutMillis>
</remoteRepository>
</remoteRepositories>
</config>
The system configuration defines:
- The local repository ext-release-local which is used to store Pineapple 3rd party libraries which isn't available in any of the public Maven libraries.
- The remote repository zk-ce which hold the publicly available ZK artifacts. The repository defines the URL: http://mavensync.zkoss.org/maven2.
- The remote repository zk-ee which hold the ZK enterprise artifacts which requires a ZK enterprise license. The repository defines the URL: http://mavensync.zkoss.org/zk/ee-eval.
The source system configuration file artifactory.config.xml is generated by configuring Artifactory maually and the exporting the configuration.
Uploading artifacts to Artifactory
The web service /artifactory/ext-release-local/path/to/jar/ is invoked with HTTP POST to install artifacts into the ext-release-local repository:
- The ZK Common library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.common:zcommon:7.0.2
- The ZK ZEL library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.common:zel:7.0.2
- The ZK library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.zk:zk:7.0.2
- The ZK Max library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.zk:zkmax:7.0.2
- The ZK Plus library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.zk:zkplus:7.0.2
- The ZK Zul library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.zk:zul:7.0.2
- The ZK web library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.common:zweb:7.0.2
- The ZK Kex library JAR and POM are installed with coordinate: org.zkoss.common:zkex:7.0.2
How to provision the build server
Create Vagrant Project
- Create Vagrant project directory: /path/to/work/pineapple-ci
- In the vagrant project directory, create a Vagrant file used to build the CI server. The Vagrant file below is included in the module xx-pineapple-dev-ssh-install-ci-linux64> in the /vagrant directory.
# -*- mode: ruby -*- # vi: set ft=ruby : BOX_NAME = ENV.fetch("BOX_NAME", "bento/centos-7.6") BOX_IP = ENV.fetch("BOX_IP", "192.168.99.10") BOX2_IP = ENV.fetch("BOX_IP", "192.168.99.11") BOX_MEM = ENV.fetch("BOX_MEM", "2048") BOX_CPUS = ENV.fetch("BOX_CPUS", "2") VAGRANTFILE_API_VERSION = "2" Vagrant.configure(VAGRANTFILE_API_VERSION) do |config| # virtual box provider specific settings config.vm.provider :virtualbox do |vb| vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--ioapic", "on"] vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--memory", BOX_MEM] vb.customize ["modifyvm", :id, "--cpus", BOX_CPUS] end config.vm.define :pineapple_ci do |ci_config| ci_config.vm.box = BOX_NAME ci_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: BOX_IP end config.vm.define :pineapple_containers do |ci_config| ci_config.vm.box = BOX_NAME ci_config.vm.network "private_network", ip: BOX2_IP end end
Organisation of tests in Pineapple
Test cases in Pineapple are organised into three groups:
- Unit tests. A unit test is an isolated test of a single class. Mocking is often used to satisfy dependencies. For information about how to write unit tests in Pineapple, see: How-to: Write unit tests in Pineapple.
- Integration tests. An integration test is a test of single class, where dependencies are satisfied using real classes. For information about how to write integration tests in Pineapple, see: How-to: Write integration tests in Pineapple.
- System tests. A system test is a integration like test with dependencies to external resources e.g. servers, containers repositories and infrastructure. For information about how to write system tests in Pineapple, see: How-to: Write system tests in Pineapple.
Configuration
Test setup for the Docker support project
The Docker support project is tested using the Docker host on the Test containers VM.
Requirements to test the Docker support project
To test the Docker support project, one Docker host must be provisioned.
The Docker host is provisioned independently of the tests, and the tests assume that the Docker host is available in a well defined state.
- Expected network configuration.
- Expected services are running.
